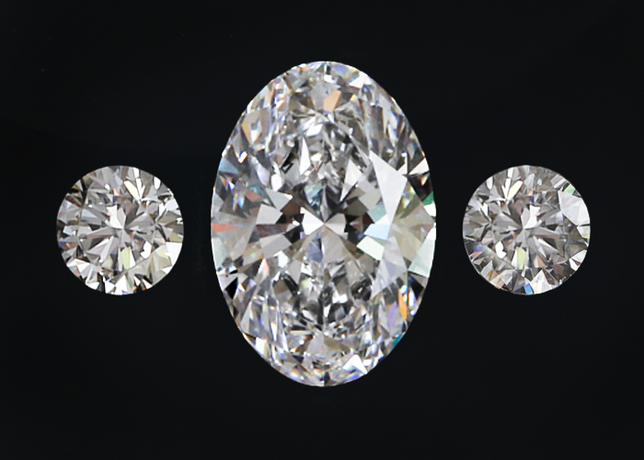
Diamonds You will Cherish for a Lifetime
A Certified Sustainability Rated Diamond is a diamond that has been independently confirmed to be in full accordance with the requirements of the SCS-007 Standard.
Climate Neutral Diamonds
This premium diamond, whether from an accredited mine or laboratory grown diamond production operation, has been evaluated and certified against five pillars of sustainability achievement.
5 Pillars of Sustainability Achievement
1. ORIGIN TRACEABILITY
Each diamond can be traced back to its source, based on advanced testing and auditing protocols, for the highest possible source-to-market certainty never before achieved.
2. ETHICAL STEWARDSHIP
Each diamond producer and handler in the chain of custody meets the most stringent social and environmental requirements aimed at providing maximum protection for workers, communities and the environment in keeping with international best practices.

3. CLIMATE NEUTRALITY
Each diamond producer agrees to eliminate or offset their entire climate footprint within a timeframe that can make a real difference. This requirement goes further than any other standard by including annual greenhouse gas emissions and additional climate pollutants, plus “legacy” emissions (that is, the residual greenhouse gases remaining in the atmosphere from prior years of operation). Because the climate can’t wait!
4. SUSTAINABLE PRODUCTION
Each diamond producer works toward achieving net zero impacts in all categories of production-related environmental and human health impacts, and is required to meet clear milestones of success along the way. This measure of sustainability has never been included in any jewelry standard, and sets an important precedent for other industries to follow.
5. SUSTAINABILITY INVESTMENTS
Targeted sustainability investments by the diamond producer support artisanal scale miners and vulnerable communities, reduce net impacts further, and contribute to a safer world. These investments demonstrate the producer’s commitment to sustainability beyond its own operations.
Revolution in Diamond Origin Assurance
1. Origin Traceability
Source Certain International (SCI) brings important breakthrough technology to the task of tracing diamonds to their source. SCI is an expert in forensic analysis, with technology so accurate that it can confirm the origin of a diamond from a specific mine shaft or from specific equipment at a laboratory grown diamond facility.
Using a sophisticated micro-scale technology known as “laser ablation inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry,” SCI identifies specific elements in a diamond that link it precisely to the source. This technology, combined with the additional checks and balances built into the system throughout the chain of custody, takes the guesswork out of a diamond’s origin once and for all.
Learn more about SCI:
www.sourcecertain.com


2. Ethical Stewardship
Developed with the help of experts on social and environmental justice, the Ethical Stewardship certification requirements ensure detailed accountability for the health, wellbeing and fair treatment of all workers, along with community and stakeholder engagement, as well as extensive protections for the environment.
These requirements are fully aligned with the strictest internationally recognized norms of business integrity, and are addressed under 12 overarching Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) principles.
12 PRINCIPLES
- Business Integrity
- Human Rights
- Worker Rights
- Free, Prior and Informed Consent
- Occupational Health and Safety
- Security
- Community Engagement
- Stakeholder Engagement
- Management of Water & Energy Resources
- Minimization of Emissions, Effluents, Wastes, Noise & Vibration
- Ecosystem Protection
- Reclamation and Closure
3. Climate Neutrality
Each year, a company’s impact on climate is caused both by its annual climate emissions and the portion of its past greenhouse gas emissions that is still hanging around in the atmosphere, or “legacy” emissions. These legacy emissions from the past are typically overlooked. The SCS 007 climate footprint is the first to account for both.
Here’s how Sustainability Rated Diamond producers become climate neutral:
- Producers work to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases and other climate pollutants from diamond production, energy consumption, and their supply chain (known in climate circles as “Scopes 1, 2 and 3”).
- Producers move further toward climate neutrality by purchasing carbon offset credits and through direct sustainability investments in strategic climate projects that reduce climate impacts through pollution prevention and other methods.
These measures often result in significant co-benefits, such as improved air quality and better health outcomes for the local population.


Taking Responsibility for the Impacts of Production
4. Sustainable Production Practices
All production operations cause impacts. Sustainability Rated Diamond producers are held accountable for all potential impacts.
The goal of sustainable production is to minimize such impacts through careful steps and innovative solutions, and to offset any remaining impacts. Diamond producers committed to SCS 007 principles are guided by the priority to do no harm, and work actively toward the goal of achieving verifiable net zero impacts across the entire life cycle.
No other jewelry standard holds producers to such a high standard.
IMPACTS ASSESSED
Climate Footprint
- Annual Emissions
- Legacy Emissions
Climate Footprint
- Regional Air Quality
- Regional Water Quality
- Hazardous Emissions
- Ocean Acidification
Climate Footprint
- Land
- Freshwater Bodies
- Marine Water Bodies
Climate Footprint
- Water
- Non-Renewable Energy
5. Sustainability Investments
Sustainability Rated Diamond producers are helping to protect the climate and environment as well as people in need through two key investments:
1. Supporting the Lives and Livelihoods of Artisanal and Small-Scale Miners (ASM) and Communities
Twenty percent (20%) of Diamond Certificate fees are being directed to support independent initiatives aimed at improving the lives of workers and protecting the environment in artisanal and small-scale mining (ASM) communities.
2. Himalayan Brick Kiln Improvement
In many countries, the only building materials available for homes and most buildings are local clay soils that can be cheaply made into bricks using primitive brick kilns. Unfortunately, these kilns represent one of the single greatest sources of potent climate and toxic air pollutants. The countries in the Himalayan Mountains watershed region have banded together under an international institution called ICIMOD, which is spearheading projects to upgrade at least 100,000 brick kilns. Producers of Sustainability Rated Diamonds are supporting these upgrades.

Diamond Certificates Tell the Sustainability Story
When you purchase a Certified Sustainability Rated Diamond you will receive a unique Certificate of Sustainability along with your diamond. This Certificate provides proof of authenticity and tells the sustainability story of the diamond. In this way, it reinforces the pedigree of the diamond with information that you will be able to treasure for years along with your beautiful diamond jewelry purchase, and pass along as an heirloom or share with others in the future.


Setting a New Standard of Excellence
SCS-007 Jewelry Sustainability Standard – Sustainability Rated Diamonds is the first truly comprehensive sustainability standard developed for the global diamond market.
Developed by SCS Standards, one of the world’s pioneers and leaders in sustainability standards, along with an international, multi-stakeholder body, this groundbreaking standard satisfies consumer demand for diamonds that meet the highest level of ethical and environmental responsibility, fully backed by third-party certification.
Certification under the standard can be sought by both mined and lab-grown diamonds to support the whole industry and consumer choice.
It also includes the entire chain of custody, establishing unprecedented benchmarks of performance and transparency. No other standard provides this level of assurance to jewelry manufacturers, retailers or clients. Learn more about the standard, developed by SCS Standards at scsstandardsdevelopment.org
Global Expert in Sustainability Standards & Certification
SCS has been leading the way in the development of environmental and sustainability standards, and the implementation of third-party certification programs, for nearly four decades (since 1984).
SCS has played a key role in the development and success of some of the world’s most prestigious standards, certification programs, and supply chain initiatives across industry sectors, such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) standard, the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) standard, USDA Organic, Non-GMO, Starbucks’ CAFÉ Practices, Environmental Product Declarations, and much more. They have been a leading certification body in the jewelry sector for the past 15 years, for programs such as FairMined, Signet, IRMA, Responsible Minerals Initiative, and LBMA and LPPM Responsible Sourcing.
SCS programs have consistently garnered strong support from civil society, as they have sought to ensure that both human rights and environmental stakeholders issues are well-represented.


Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is a Sustainability Rated Diamond?
A Sustainability Rated Diamond is a diamond from an accredited natural or laboratory grown diamond production operation that has been evaluated against five pillars of sustainability achievement and is found to be in full conformance with the requirements of the SCS-007 Jewelry Sustainability Standard – Sustainability Rated Diamonds.
Q: What’s the difference between certification and accreditation
Individual diamonds are certified and tracked from source to market through the chain of custody. Companies that produce or handle the diamonds are accredited, based on conformance with the Producer and Handler requirements of the Standard. Companies that provide testing and grading services are required to undergo technical accreditations to ensure competence in the delivery of these crucial services.
Q: How was the SCS-007 standard developed?
SCS-007 was developed under an international, multi-stakeholder process facilitated by SCS Standards, the non-profit standards development arm of Scientific Certification Systems, Inc. Stakeholders were recruited from multiple sectors, including diamond production, diamond handling and retail, diamond grading and technology, academia, and civil society.
Q: Are international guidance and norms referenced by the standard?
The criteria in the SCS-007 standard reference numerous international documents that have been developed to provide guidance for best practice in social and environmental responsibility.
Q: What makes SCS-007 a leadership standard?
SCS-007 picks up where other standards leave off, making it the most comprehensive standard for diamonds ever established. Under each of the five pillars, it sets unparalleled benchmarks of performance:
- Testing protocols capable of tracking diamonds back to a specific mine shaft or piece of laboratory equipment, with sufficient checks and balances across the entire chain of custody from source to market, backed by thorough surveillance auditing and sampling, to achieve 99.9% origin assurance.
- Conformance with stringent environmental, social and governance (ESG) criteria under twelve major principles of ethical stewardship.
- Climate neutrality conformance that: 1) encompasses all greenhouse gas pollutants plus other major climate pollutants commonly overlooked; and 2) addresses both current and “legacy” emissions to capture the complete climate footprint.
- Elimination or offsetting of impacts across the production life cycle, to reach net-zero impacts in environmental and human health impact categories over specified timeframes.
- Sustainability investments that support artisanal and small-scale miners, provide a wide range of societal benefits, and further protect the environment and climate.
 Solitaire
Solitaire
 Solitaire with Pavé
Solitaire with Pavé
 Bezel Set
Bezel Set
 Halo
Halo
 Multistone
Multistone
 Unique
Unique
 Nature Inspired
Nature Inspired
 Everyday
Everyday
 Wider Band
Wider Band














